Introduction
Occasionally, we recieve tickets about puzzling disk space usage. There’s usually a pretty simple explanation for this issue, and it’s also straightforward to get to the bottom of when you know where and how to look. This article will help you get to the bottom of these issues.
Table of Contents
Why Disk Space Warnings are Important
Allowing your server’s disk space to fill up can have serious consequences. If you haven’t already, we recommend setting up Slack notifications for your account:
How to set up Slack Notifications
At best, MySQL won’t have enough memory to function and will go offline, taking all of your websites offline. At worst, you’ll suffer irreversible database corruption. In this case, you’ll need to restore a server snapshot or restore your websites from backups to another server.
These types of issues are beyond our scope of support. Make sure you’re monitoring your server notifications and either increase your server size accordingly or free up disk space by deleting unnecessary files or moving large websites to a different server.
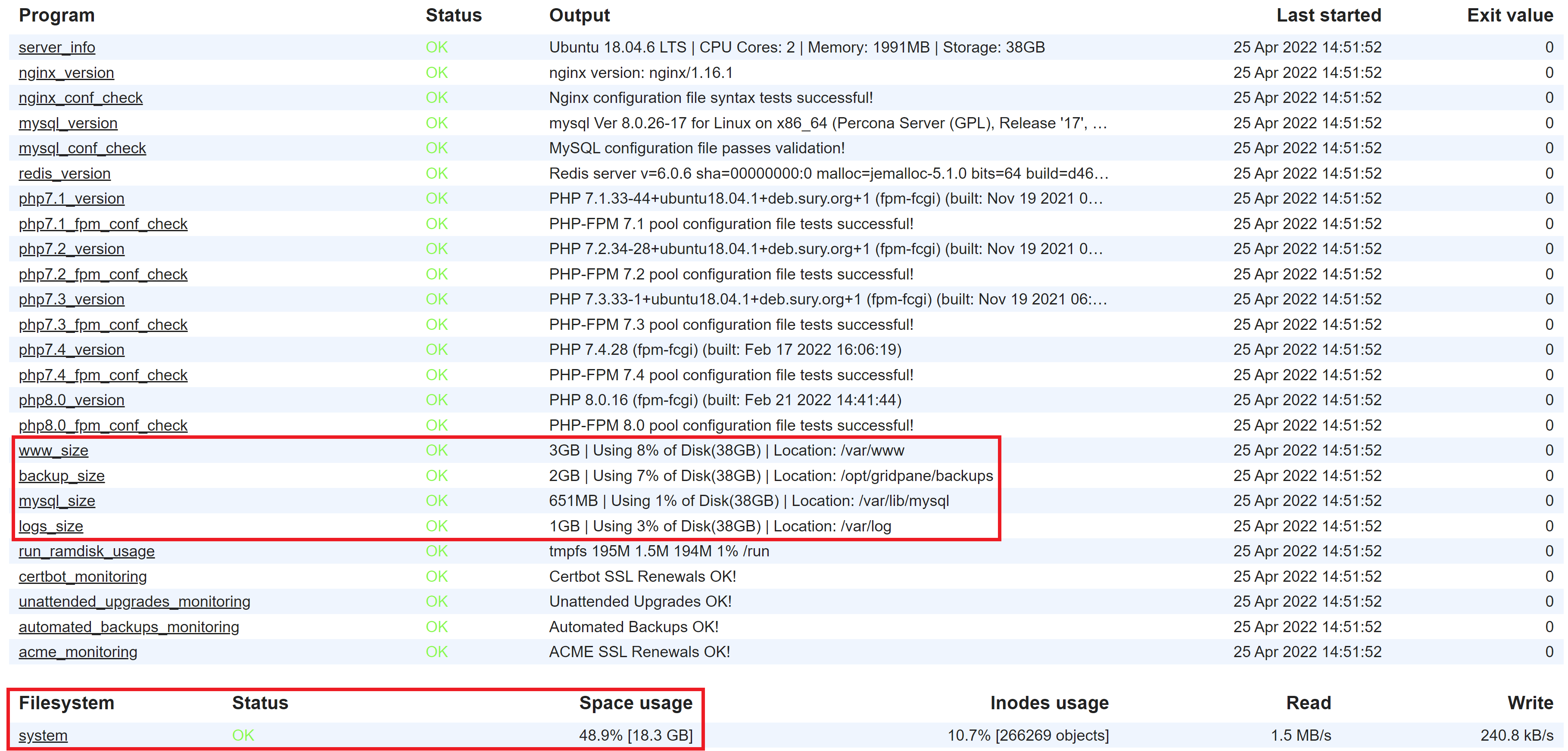
Monit Stats
The first place to check is your server’s Monit stats. Here you can see your disk space size, MySQL size, backup size, and log size:
In the beginning…
After the approximately 10GB of space taken up by the Ubuntu OS and our systems, the rest is your website files, their databases, website/server logs, and your local website backups.
Where and How to Check for Disk Space
Checking Monit like in the above screenshot above may make it obvious pretty quickly where you need to first begin checking. The following requires connecting to your server – please see the following guides to get started:
Step 1. Generate your SSH Key
Step 2. Add your SSH Key to GridPane (also see Add default SSH Keys)
Step 3. Connect to your server by SSH as Root user (we like and use Termius)
If the server has been live for an extended period then other logs not just inside /var/log can build up as well – especially if you have numerous sites on the server.
The three main directories are:
/var//opt//etc/
You’ll specifically want to check:
- Your backups
- Your websites /wp-content directory
- Your database sizes
- Server logs
- Site logs
You can narrow down large directories and files with the following two commands.
The first lists directory sizes (largest size at the bottom, along with the directory total size):
du -h --max-depth=1 | sort -h
The second lists files inside a directory in order of size (again with the largest at the bottom):
ls -laShr
Most Common Causes
- One or more of your websites (files or database) is much larger than expected.
- Lots of plugin-created backups are consuming a high amount of disk space.
- An old staging site is much larger than expected.
Check Your Website File Sizes
You can check your website sizes by first navigating to their directory:
cd /var/www
And running:
du -h --max-depth=1 | sort -h
Check Your Website Database Sizes
You can check individual database sizes with the following:
cd /var/lib/mysql
du -h --max-depth=1 | sort -h
Freeing Up Disk Space
Important: If you’re unsure if a file is important or not, don’t delete it. The best thing you can do is post in the community forum where our team or the wider community can provide an answer for the file in question, and everyone in the wider community can benefit.
Deleting Files
If you’ve identified files than are no longer needed, you can remove them with the rm command. For example, in the directory where the file exists, you can use the following:
rm bigfilename.here
Deleting Directories
Please exercise caution when deleting entire directories. This kind of action is irreversible and will require you to make use of a backup to rectify the issue. You can remove directories with the rm command with the -r flag. This will remove non-empty directories and all of the files inside them recursively. For example:
rm -r directorynamehere
Database Optimization
If any of your databases are far larger than you expected them to be, you may be able to reduce their size significantly by optimizing them.
Purging Some Backups
For more details on backups and disk space, please see part 3 of our backups troubleshooting article:
V2 Backups Part 4. Troubleshooting & Backups Failure Notifications
Important
Be sure to backup your database (or ensure you have current website backups) before making significant database changes, such as running an optimization. Risks of things going wrong are extremely small, but it's important to ensure you have a backup just in case.
You can do this with a plugin like WP Sweep, the LS Cache plugin, Perfmatters, or other actively maintained and highly reviewed optimization plugins.
You can also use WP-CLI. On GridPane, you can use GP WP-CLI as follows (replacing site.url with your websites URL):
gp wp site.url db optimize
System Users and Disk Space
Disk space issues caused by an excessive amount of system users (that don’t actually own a website) is a much rarer case than any of the causes detailed above.
However, if you’ve had a lot of websites on a server over time, with many of them being moved to another server, these leftover system users can take up a surprising amount of space if you haven’t been proactively deleting them, even with no websites attached.
You can check this by navigating to your home directory with:
cd /home
And then you can list your system users by size with:
du -h --max-depth=1 | sort -h
Here you’ll see ALL of your servers system users. Please note than many or even all of these users may own a website, so don’t edit or delete anything unless your absolutely sure the system user in question is no longer needed.
The .wp-cli directory for system users that don’t own a website is likely what’s consuming the disk space.
Deleting System Users
Important
As stated above, don't delete system users or any files associated with them if they still own any websites on your server. We recommend deleting them from within your GridPane account as they're are guards in place that will prevent you from deleting a user's that owns one or more of your websites on that server.
Please refer to this article for instructions on how to remove system users from your servers: