Introduction
This is one of the more common, and more scary WordPress errors, but it can usually be solved pretty quickly. Below is our guide to diagnosing and fixing the database connection errors on your WordPress sites.
For those very rare cases where it can’t be solved, such as Malware/hacks that can’t be undone, you’ll need to make use of a backup.
Table of Contents
Quick First Checks:
- Always Check Monit
- Server: MySQL is Down
- Server: MySQL needs more memory
- Server: Your disk space usage is above 90% and starving services of memory
Website Checks:
- Website: Database tables are locked
- Website: Connection pool is exhausted
- Website: Database is corrupt
- Website: Your database login credentials and/or table prefix are incorrect
- Website: Your site has been hacked
MySQL is Corrupt:
Some of the following may require you to SSH into your server. Please see these guides to get started:
Step 1. Generate your SSH Key
Step 2. Add your SSH Key to GridPane (also see Add default SSH Keys)
Step 3. Connect to your server by SSH as Root user (we like and use Termius)
Always Check Monit
First things first before we begin: Always check Monit when you experience any kind of error to see if there’s an obvious cause at the server level. To open Monit head to your server page and click on the green icon button.
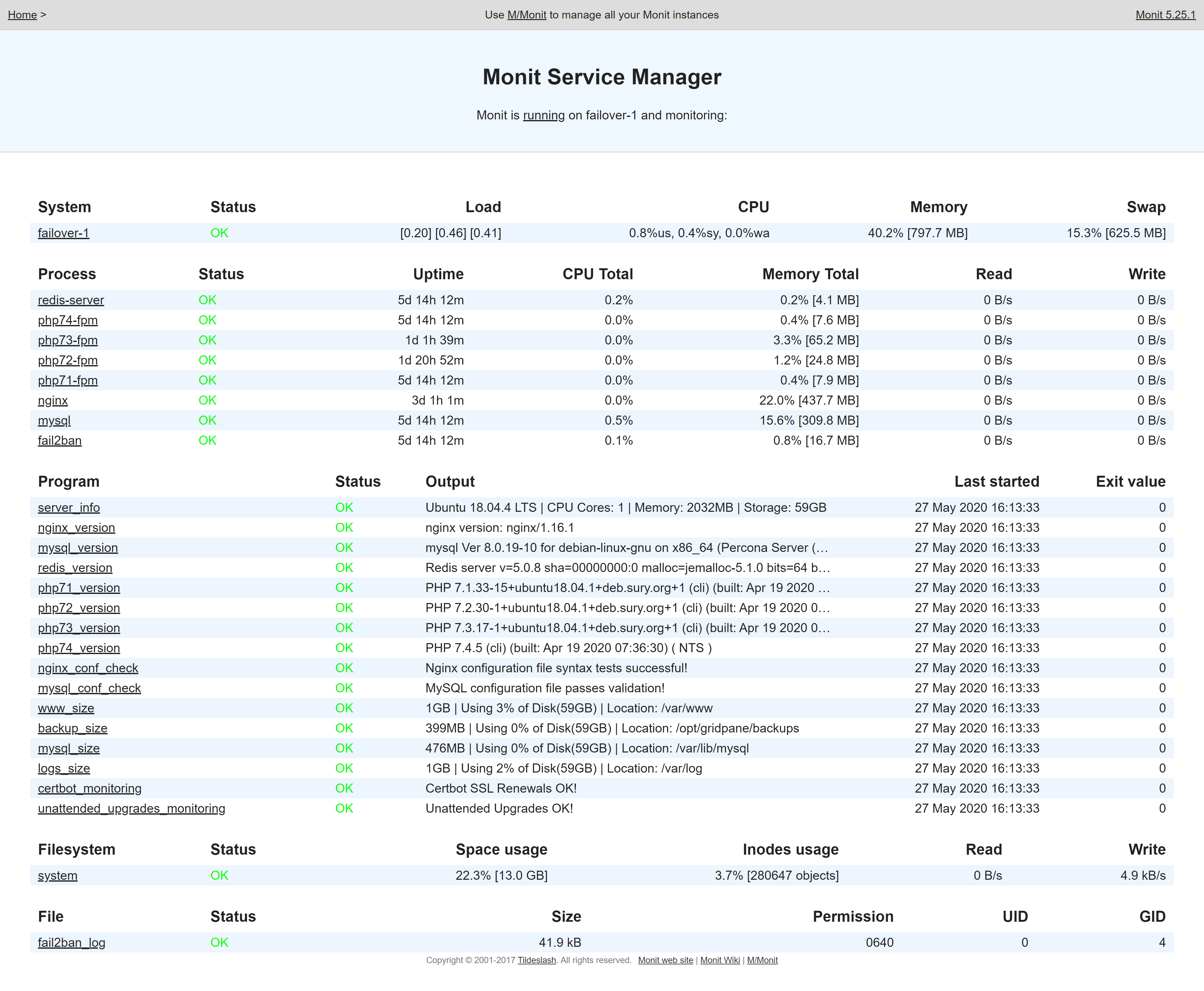
This will open up a window with all your server stats. This is what a healthy server looks like:
1. MySQL is Down
The Problem
MySQL is down on your server and none of your website’s databases are accessible, resulting in all of your websites having the “Error Establishing a Database Connection” message.
Diagnosis
Open up Monit for your server. What is MySQL’s Status? If it’s anything other than “OK” then this may be the source of your problem.
How to Fix it
First SSH into your server – please see the links to our guides at the beginning of this article to get started.
Check if MySQL is running with this command:
service mysql status
If MySQL is not running, you can start it with this command:
service mysql start
If MySQL doesn’t start then it will give an error explaining what’s happening, and you next need to contact us on support with your server IP and details of the error.
2. MySQL needs more memory
The Problem
You keep experiencing slow performance and frequent (but not constant) database connection errors.
Diagnosis
MySQL needs more memory and keeps restarting causing temporary outages. First, we need to know if MySQL on your server is up and running, and whether it’s healthy. Open up Monit and look at MySQL’s memory usage and uptime. When looking at uptime compared to the other services, has MySQL been restarted recently? If yes, then it may be hitting its memory allocation over and over and being restarted by Monit.
How to Fix it
There’s not a clear cut and dry solution, but you should first try increasing MySQL’s memory allocation.
To begin, run the following command
nano /etc/monit/conf.d/mysql
Typical file:
Check process mysql with pidfile /var/run/mysqld/mysqld.pid
group database
group mysql
start program = "/usr/sbin/service mysql start"
stop program = "/usr/sbin/service mysql stop"
if cpu > 60% for 2 cycles then alert
if cpu > 70% for 3 cycles then exec "/usr/local/bin/gpslack MYSQL_HOT warning"
if cpu > 90% for 5 cycles then restart
if mem > 550 MB for 3 cycles then restart
if failed host localhost port 3306 protocol mysql with timeout 15 seconds for 3 times within 4 cycles then restart
if failed unixsocket /var/run/mysqld/mysqld.sock protocol mysql for 3 times within 4 cycles then restart
if 3 restarts within 5 cycles then exec "/usr/local/bin/gpslack MYSQL error"To adjust MySQL’s memory limit adjust this line, for example:
if mem > 750 MB for 3 cycles then restart
Please keep in mind that the more memory you allocate to MySQL, the less will be available for your server’s other processes, and this may create a whole new load of problems. We’d recommend small increases up to the 50% of the total memory mark, and if you’re still experiencing issues after that, you need to look at your database performance or increase your server size.
Once you’ve adjusted the above line, hit Control+O, then enter to save the file. Then Control+X to exit nano.
Next, you need to reload Monit:
monit reload
Test and repeat, then continue below if necessary.
3. Your disk space is above 90%
The Problem
If your disk space usage is close to full, especially on servers that have a smaller amount of memory, then this may be the cause of multiple issues on your server, including slow performance and 504 timeouts.
Diagnosis
MySQL may be being starved of memory – as may other services on your server.
How to Fix it
The fix is to either clear up some space on your server or resize your server at your IaaS provider.
You can check which websites are the largest on your server by running:
cd /var/www
And then:
du -h --max-depth=1 | sort -h
With this information, you can begin investigating any websites that look larger than they should be.
You can also reach out to support for help clearing out local backups on your server and any unnecessary binlogs.
4. Your websites database tables are locked
The Problem
If our soon-to-be-replaced backup system is running it’s possible that it’s locking up your database.
Diagnosis
To check if you have locked database tables, SSH into your server and run the following command:
gp mysql login root
Now logged into MySQL, check your active processes with:
show processlist;
If you see “Waiting for table metadata lock”, you’re experiencing table locking. Here’s an example of what this looks like:
mysql> show processlist;
+-------+---------------------+-----------+---------------------+---------+--------+---------------------------------+------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+-----------+---------------+
| Id | User | Host | db | Command | Time | State | Info | Rows_sent | Rows_examined |
+-------+---------------------+-----------+---------------------+---------+--------+---------------------------------+------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+-----------+---------------+
| 5 | event_scheduler | localhost | NULL | Daemon | 558150 | Waiting on empty queue | NULL | 0 | 0 |
| 34478 | VOO_example_com | localhost | VOO_example_com | Sleep | 70388 | | NULL | 0 | 0 |
| 34479 | VOO_example_com | localhost | NULL | Sleep | 70388 | | NULL | 6230 | 6230 |
| 34480 | VOO_example_com | localhost | NULL | Sleep | 70387 | | NULL | 748034 | 748034 |
| 40581 | VOO_example_com | localhost | VOO_example_com | Query | 14241 | Waiting for table metadata lock | DROP TABLE IF EXISTS wp_bv_ip_store | 0 | 0 |
| 40582 | VOO_example_com | localhost | VOO_example_com | Query | 14140 | Waiting for table metadata lock | DROP TABLE IF EXISTS wp_bv_ip_store | 0 | 0 |
| 40583 | VOO_example_com | localhost | VOO_example_com | Query | 14040 | Waiting for table metadata lock | DROP TABLE IF EXISTS wp_bv_ip_store | 0 | 0 |
| 40984 | VOO_example_com | localhost | VOO_example_com | Query | 12582 | Waiting for table metadata lock | SELECT * FROM wp_bv_ip_store WHERE '�<:' >= `start_ip_range` && '�<:' <= `end_ip_range` && `is_lp` | 0 | 0 |
| 40985 | VOO_example_com | localhost | VOO_example_com | Query | 12518 | Waiting for table metadata lock | SELECT * FROM wp_bv_ip_store WHERE '�<:' >= `start_ip_range` && '�<:' <= `end_ip_range` && `is_lp` | 0 | 0 |
This particular example was MalCare, which shares the same table prefix with Blogvault – another plugin we’ve seen at the cause. Other plugins we’ve seen include Cleantalk, Rank Math, and WPvivid.
Exit MySQL with:
exit
How to Fix it
You can restart MySQL with the following command:
gp mysql restart
You can also restart MySQL inside of Monit as well.
This is something we frequently see with WaaS networks. You’ll want to ensure that your using InnoDB and not MyISAM, and then determine whether this is related to our backup system.
If you’re experiencing these issues around the start of every hour, this is likely related to your backup system, Borg, running and locking your tables while it takes the backups. If you have a large website that takes a long time to backup, this could frequently impact your performance for extended periods of time.
You can also learn how to change your backup schedule here:
5. Connection pool is exhausted
The Problem
Sometimes connection errors are related to database table locking as above, but it can also be if you simply have a lot of connections, and your website can’t handle the load. SQL is limited to 150 connections, and when it hits that, it will block new connections and will result in an error.
Diagnosis
SSH into your server and run the following command:
gp mysql login root
Now logged into MySQL, check your active processes with:
show processlist;
You can also check connections with:
show status like '%onn%';
What you’re looking to determine is whether your database is being swamped with tasks that it’s unable to keep up with.
2021-03-31T12:26:46.407886Z 38351 [Warning] [MY-000000] [Server] Too many connections
2021-03-31T12:26:48.164792Z 38352 [Warning] [MY-000000] [Server] Too many connections
2021-03-31T12:28:04.670871Z 38355 [Warning] [MY-000000] [Server] Too many connections
2021-03-31T12:29:15.297826Z 38356 [Warning] [MY-000000] [Server] Too many connections
...
2021-03-31T12:29:24.812716Z 38357 [Warning] [MY-000000] [Server] Too many connections
Hundreds of queries may mean that causing queries to not able to finish fast enough. MySQL slow logging may be able to help.
How to Fix it
You need to take a look at your caching strategy. We highly recommend you check out our native server caching options and definitely enable Redis Object caching on your website.
This will dramatically reduce the amount of work your database has to perform, which will decrease your server load and allow your website to handle significantly more traffic.
To fix the immediate problem, you can restart MySQL with:
gp mysql restart
6. Your Database is corrupt
The problem
If the error is only on the wp-login page then it’s highly likely that the database needs a repair.
If it’s on every page then it may still be a corrupted database but require extra investigation.
Diagnosis
Head to yourdomain.com/wp-login.php. Does this offer any more information? For example, “One or more database tables are unavailable. The database may need to be repaired”. If yes, then your database needs to be repaired.
If you’re seeing the error across all your websites pages and still see the same error on your login page, then you can run a check via WP-CLI, outlined in the Repairing your database via WP CLI section below.
How to Fix It
You will need to access your website via SFTP, or SSH into your server to run a database repair. Below will walk you through the steps for each. Before running a repair, ensure you have a backup. Here’s our article on backing up and exporting/importing databases:
How to backup / export / import a WordPress database
REPAIRING YOUR DATABASE VIA WP-CONFIG.PHP
To repair your database via wp-config.php, you’ll need to connect to your server over SFTP. To do this, please see the following guides to get started (you only need to follow one of them):
Connect to a GridPane Server by SFTP as Root user
Connect to a GridPane Server by SFTP as System User
Once you’ve connected to your server navigate to your website’s directory under www/yourdomain.com.
Here you’ll need to down your wp-config.php, and open it in a text editor. Add the following code just above the line that says “That’s all, stop editing! Happy blogging“.
define('WP_ALLOW_REPAIR', true);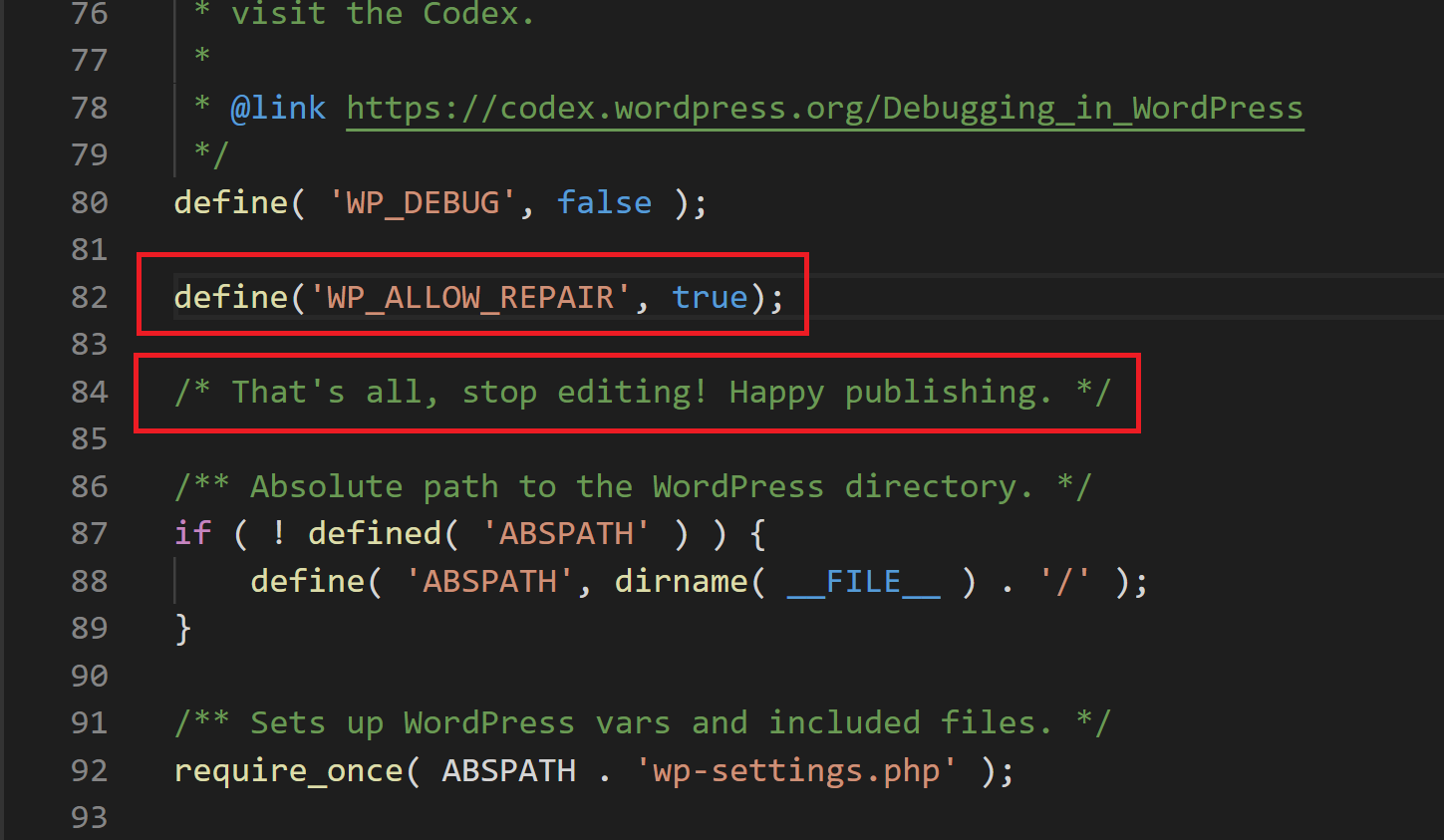
Now re-upload your wp-config.php file and head over to yourwebsite.com/wp-admin/maint/repair.php
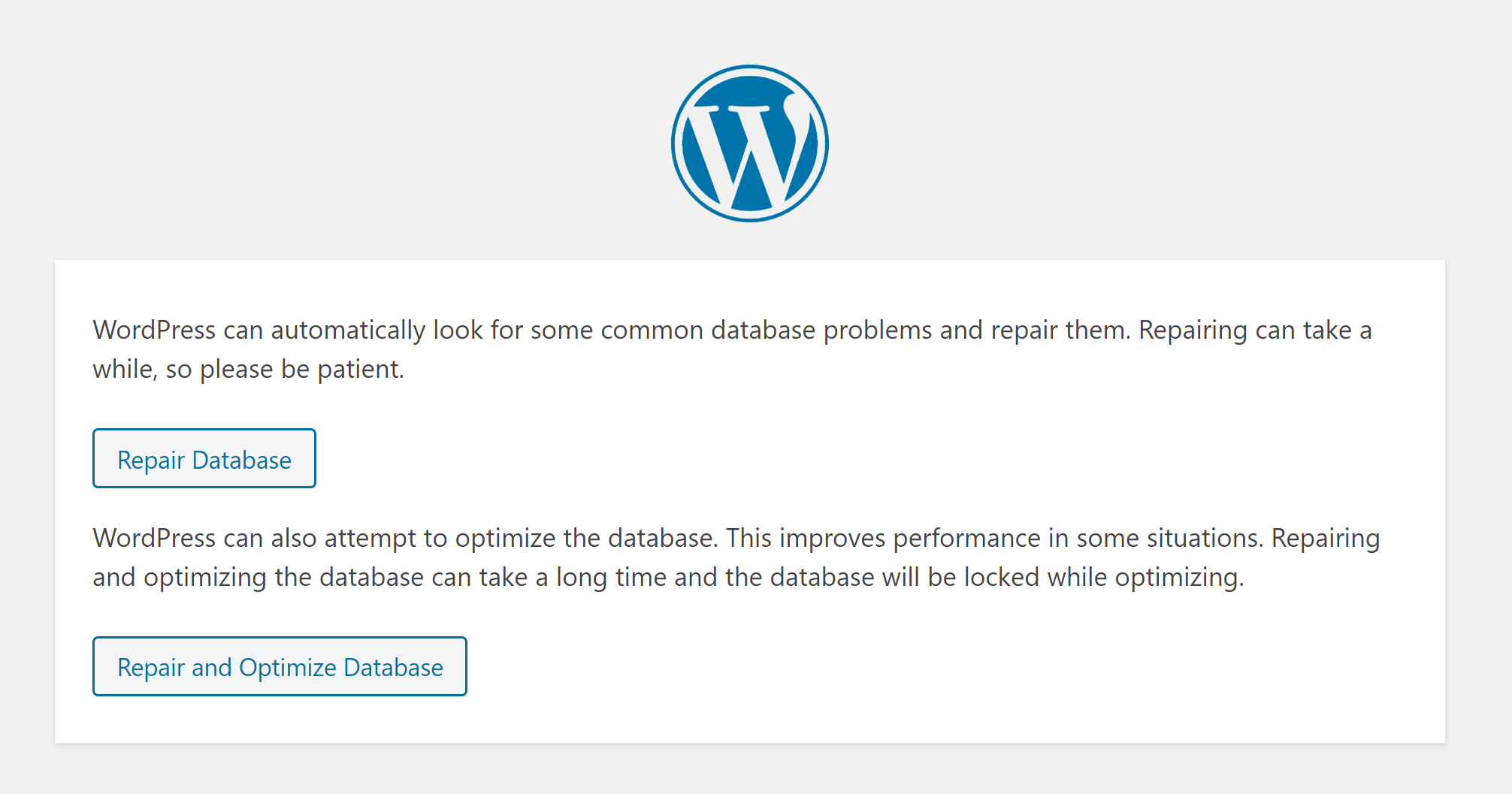
Note: Anyone can access the database repair page. Once you’ve finished repairing your database, make sure you go back and remove this code from your wp-config.php.
REPAIRING YOUR DATABASE VIA WP CLI
First, navigate to your websites htdocs directory with the following command (switching out “site.url” for your domain name):
cd /var/www/site.url/htdocs
Then run a check with:
gp wp {site.url} db checkYou’ll probably find crashed tables. Then do the repair with the following (but always take a backup first!):
gp wp {site.url} db repairREPAIRING YOUR DATABASE VIA PHPMYADMIN
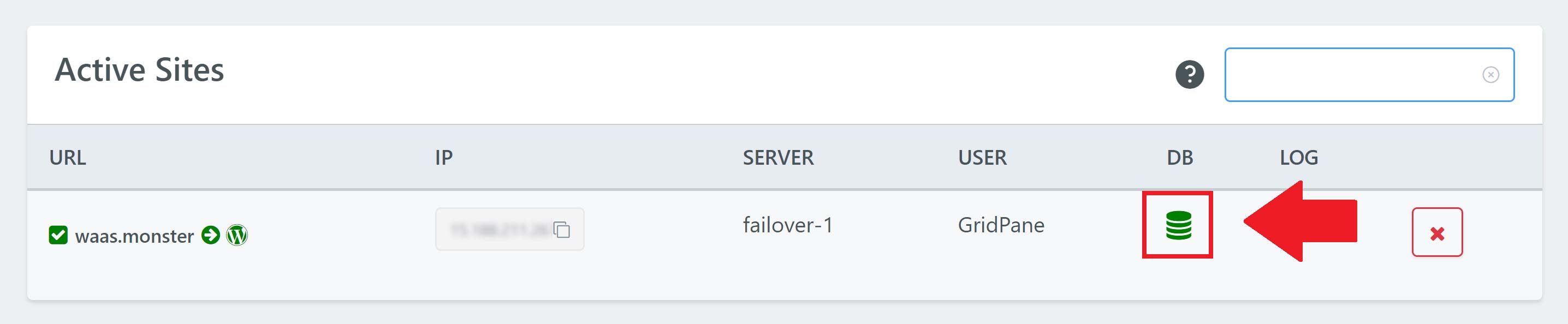
Please note that this method will not work for the InnoDB storage engine, which we use by default at GridPane.
To begin, head to your account and open up phpMyAdmin by clicking the database icon next to your website.
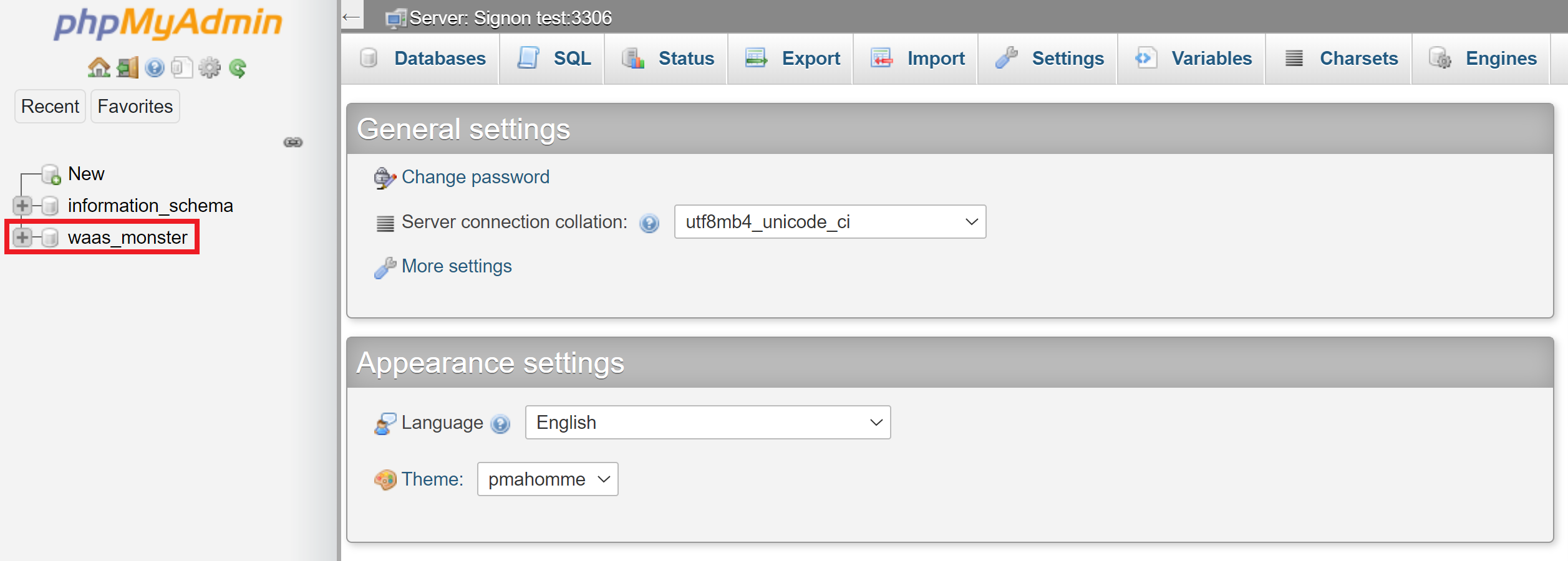
Inside phpMyAdmin, click on your database name in the left-hand column:
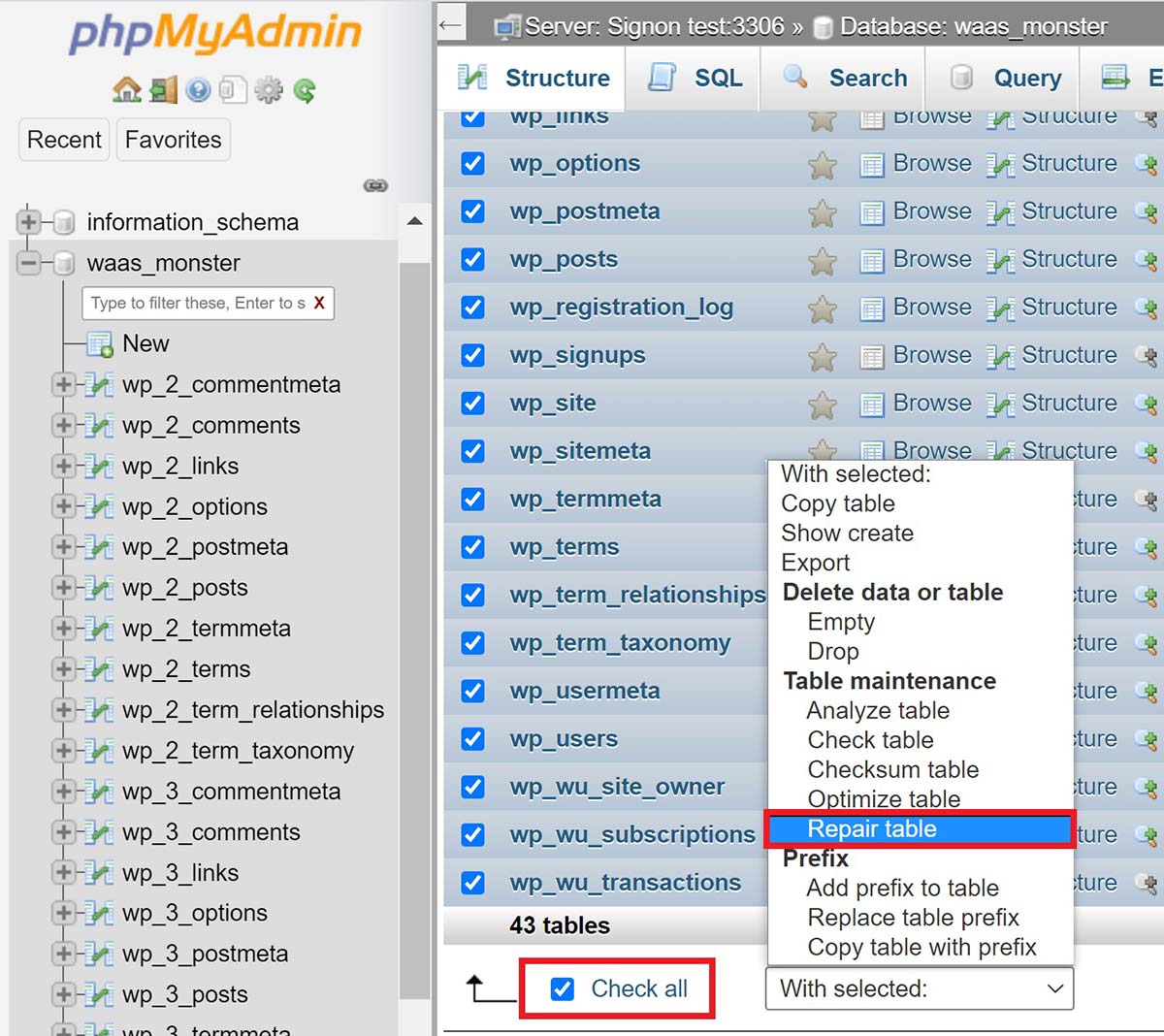
Scroll down and check the “Check all” check box, and select “Repair” from the dropdown.
7. Incorrect Database Credentials and/or Table Prefix
The Problem
You’ve migrated your website in but you’re experiencing an “Error Establishing a Database Connection” or 504 timeouts.
Diagnosis and Solution
Here we want to check the following things: –
- Is the table prefix correct?
- Is there another wp-config.php in htdocs?
- Is your database name correct?
- Inside your databases wp_options table is the site URL and home URL correct?
- Do the database username and password match those in your websites wp-config.php?
For example purposes, we’ll use a real domain: “waas.monster”.
To begin, head to your account and open up phpMyAdmin by clicking the database icon next to your website.

Inside phpMyAdmin, click on your database name in the left-hand column:

Next, back inside your GridPane account, open up your wp-config.php file by opening up your website’s configuration modal and clicking “Display wp-config” button:
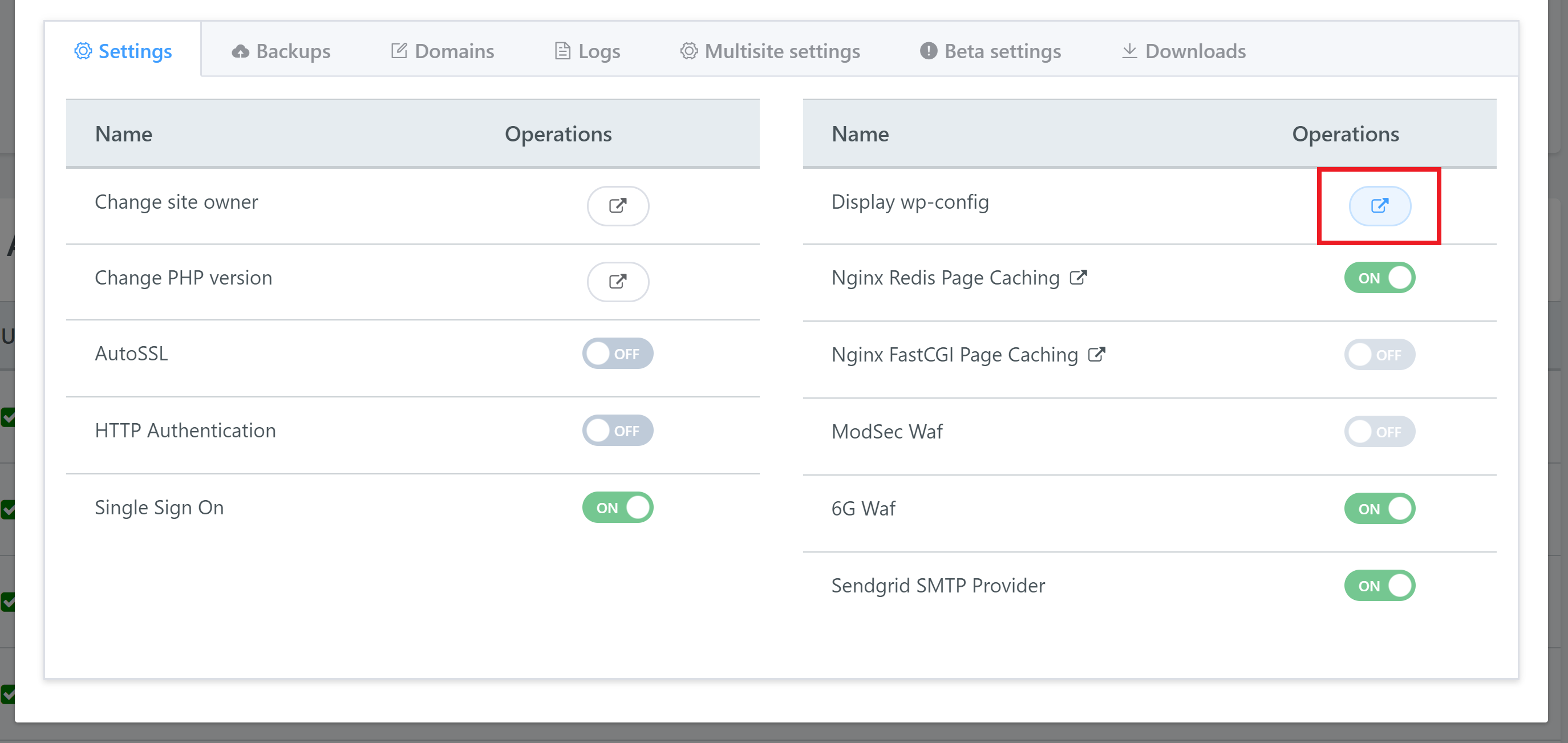
We can now begin our checks.
STEP 1. IS YOUR TABLE PREFIX CORRECT?
Does your database table prefix match
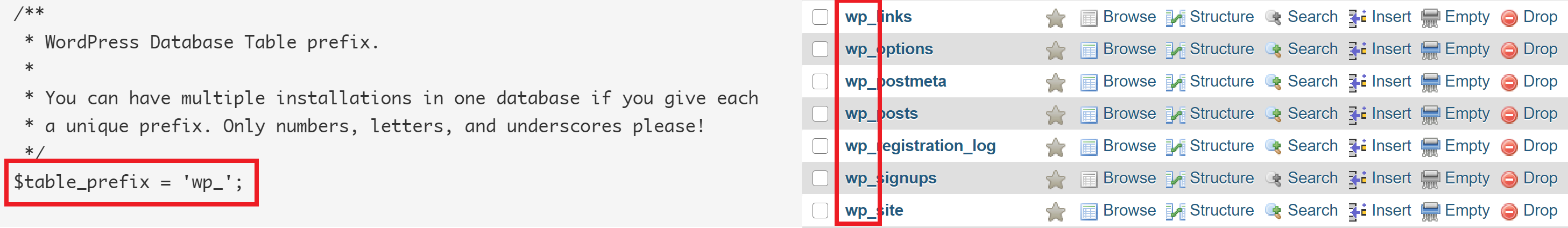
Solution: If your table prefix doesn’t match up, but all your database tables are using the same prefix, you can edit the table prefix in your wp-config.php via SFTP (download, edit, re-upload) or the command line.
To edit via the command line type the following command (switch out “site.url” with your domain name):
nano /var/www/site.url/wp-config.php
Edit your prefix and then hit Control+O, and then enter to save the file. Exit with Control+X.
STEP 2. IS THERE ANOTHER WP-CONFIG.PHP IN HTDOCS?
If there’s a separate wp-config.php in your htdocs it’s likely this is the cause of your broken website.
To check, SSH into your server and navigate to your htdocs directory. Via the command line you can use the following (switch out “site.url” with your domain name):
cd /var/www/site.url/htdocs
Then run:
ls -l
This will list all of the files here. wp-config.php should NOT be one of them.
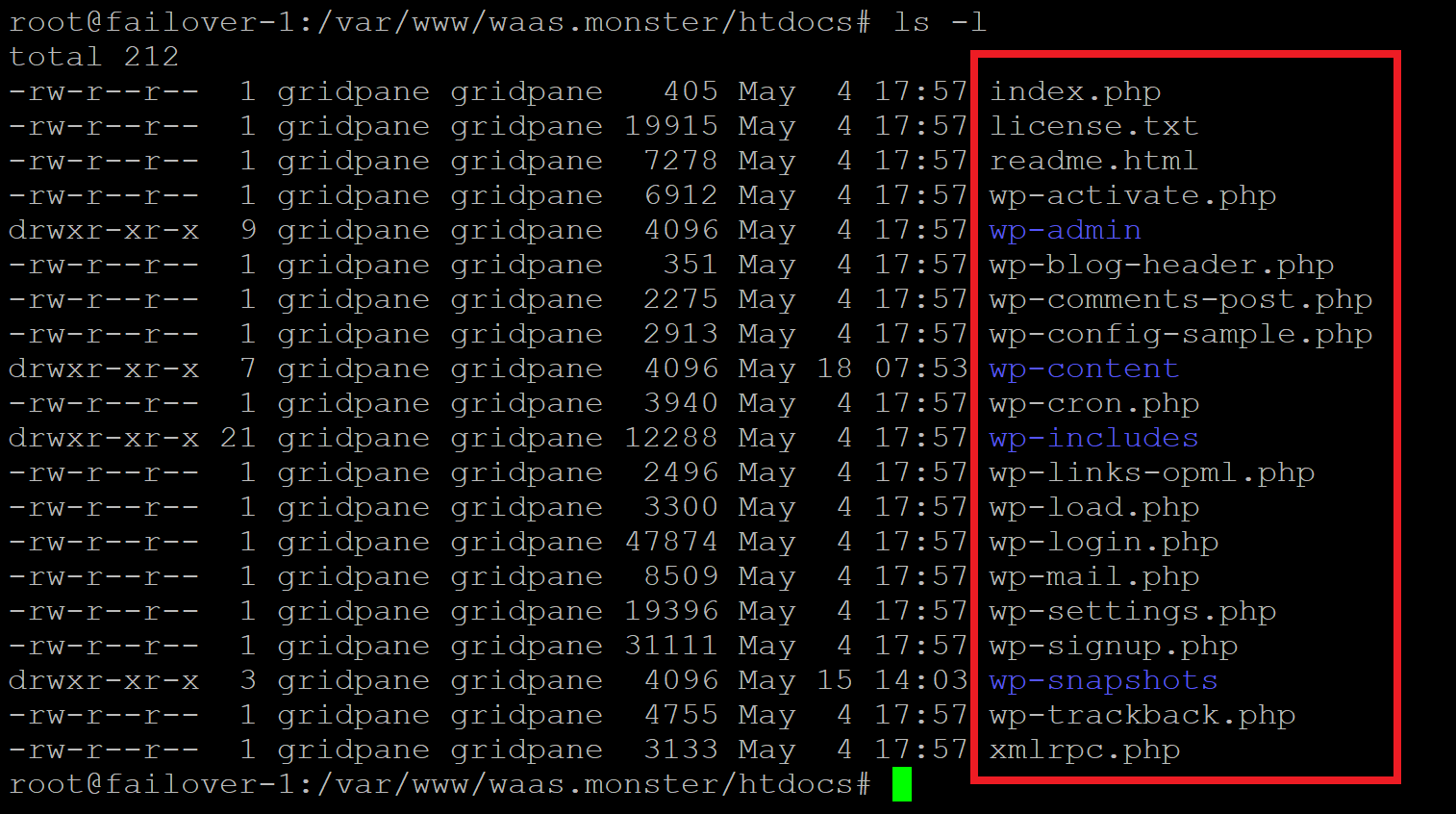
STEP 3. IS YOUR DATABASE NAME CORRECT?
Does your database name inside phpMyAdmin match with the one inside your wp-config.php file?
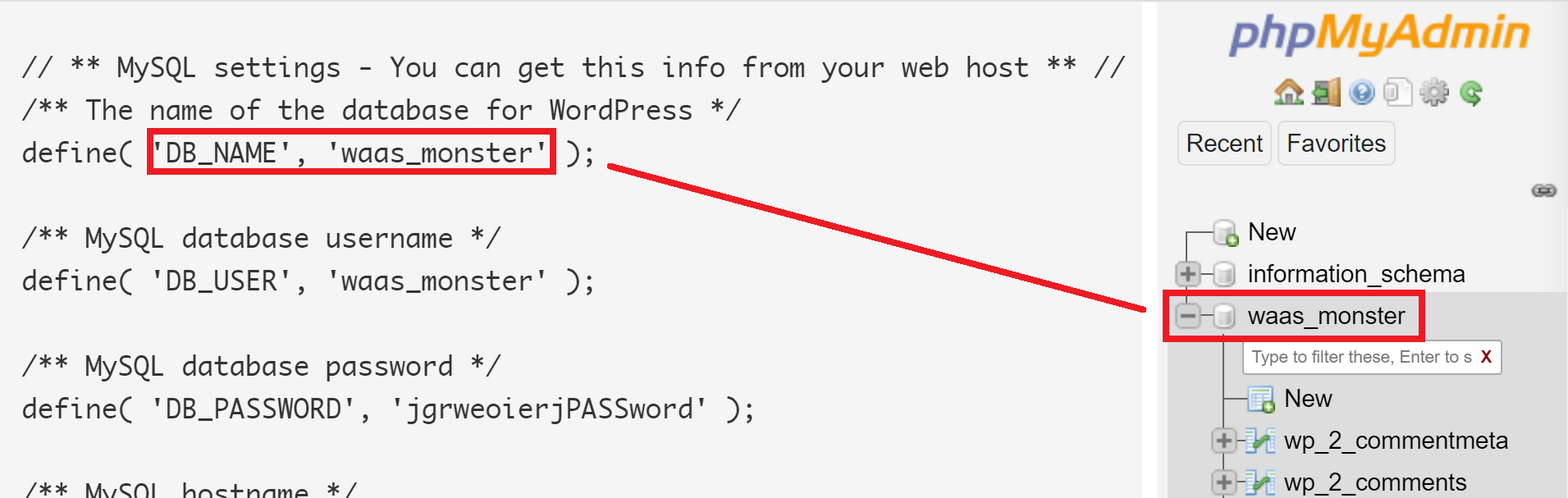
If it’s correct, move on to step 4.
If it’s incorrect there’s a good chance that our wp-config.php has been replaced during a migration, wiping out the database details. Move on to step 5.
STEP 4. ARE THE SITE URL AND HOME URL CORRECT?
Find your wp_options table and click into it. Do these details match your website’s domain?
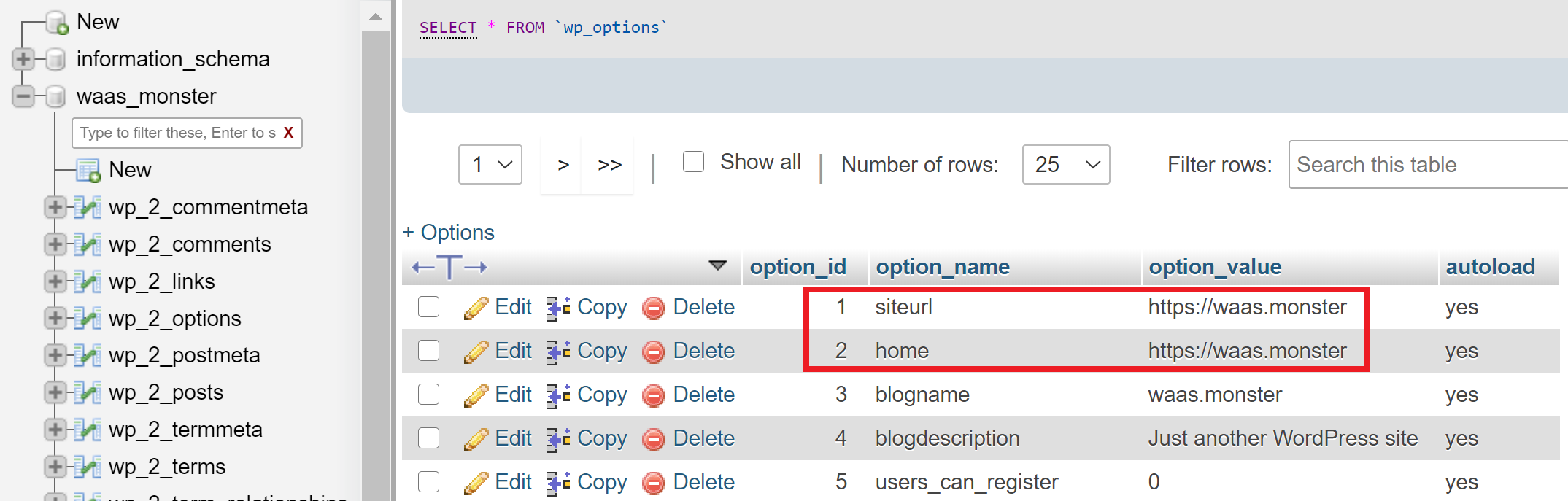
If these are incorrect, double click on the address in the option_value column to edit, and then hit enter to save it.
STEP 5. DO THE DATABASE USERNAME AND PASSWORD MATCH THOSE IN YOUR WEBSITES WP-CONFIG.PHP?
If all of the above is correct, but you’re still getting the error then the next step is checking your database username and password. For this, you’ll need to SSH into your server.
We’re going to test to see if we can connect to the database directly using the details provided in the wp-config.php file.
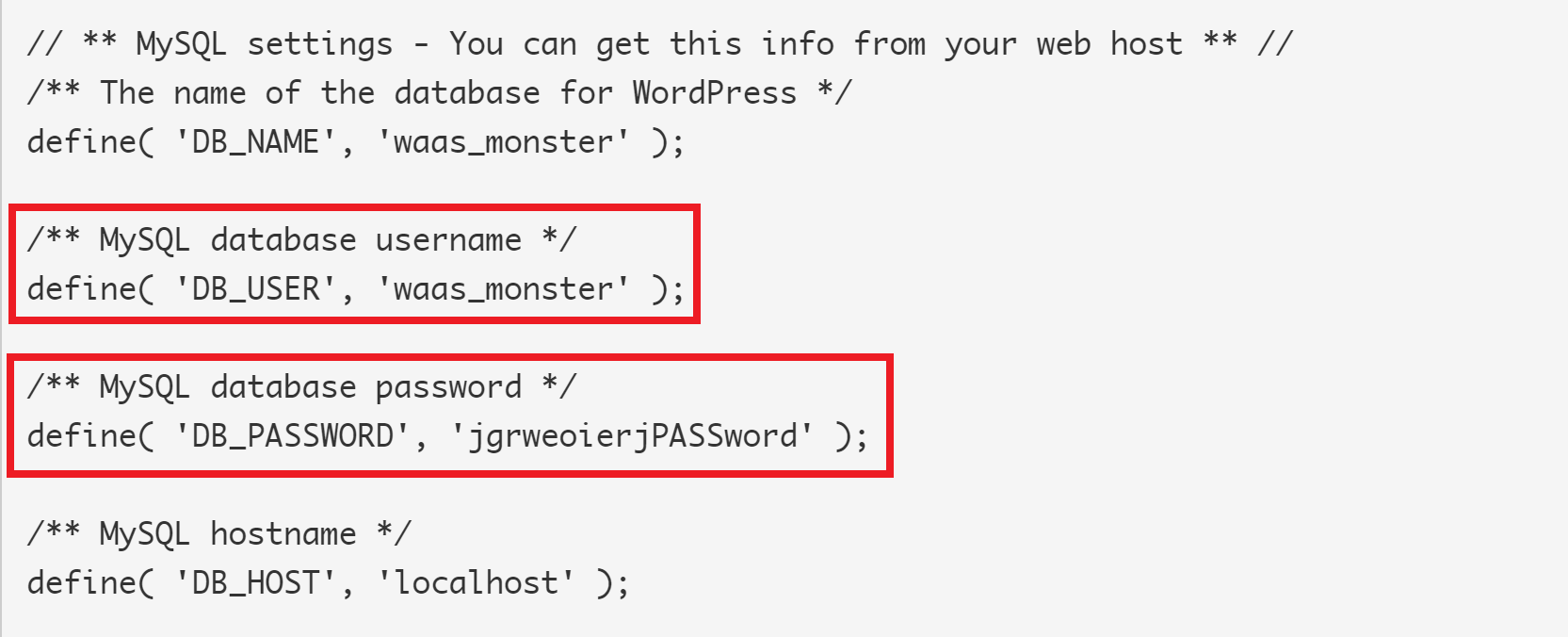
First, run the following command, switching out “USERNAME” with your database username:
mysql -u USERNAME -p
You’ll be prompted for your password, here you need to copy and paste your database password.
If your details are correct, you’ll see a message that says “Welcome to MySQL Monitor” as show below. You can also check your database name here with:
show databases;
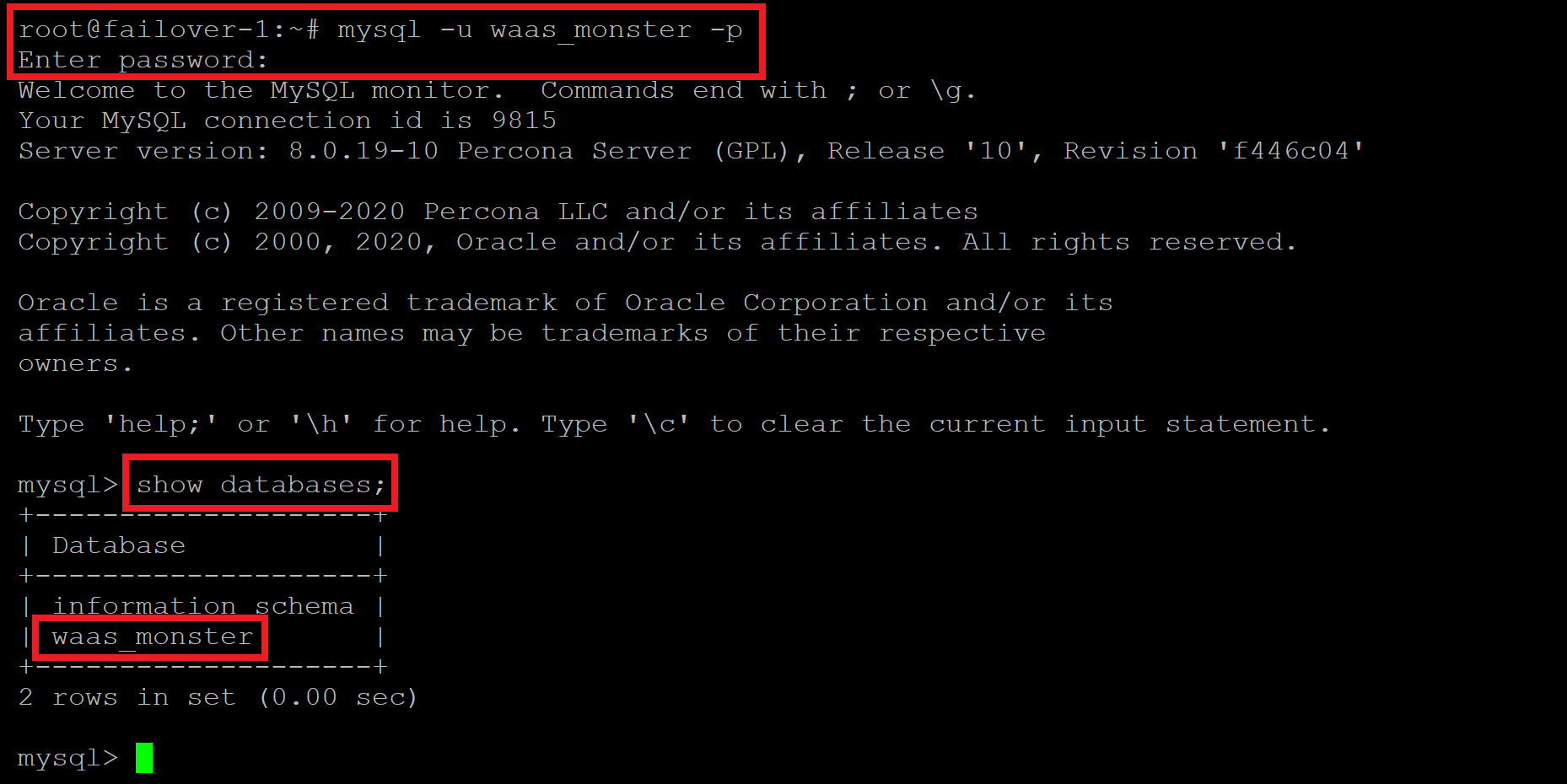
If they don’t match, then it’s likely that our wp-config.php has been overwritten.
You should be able to access a backup of your wp-config file by SSH’ing into your server and running the following command (switch out “site.url” with your domain name):
nano /opt/gridpane/site-configs/site.url-wp-config-immutable.BUP
Example:
nano /opt/gridpane/site-configs/gridpane.com-wp-config-immutable.BUP
Here you can copy the contents and add the correct details to your website’s wp-config.php file.
8. Your website has been hacked
The Problem
Your website is acting strange, slow, you’re unable to login, pages have been altered, frequent or constant database connection error etc etc. There are many potential symptoms you experience from a hack/malware infection.
Diagnosis
To check if you’ve been hacked, the best solution is to run an effective malware scanner on your site. If you have a developer account we can run our malware scanner for you, or you can use one of the many great security plugins to run a malware scan.
An Introduction to Maldet and ClamAV Malware Scanning
How to Fix it
If you’ve had a website infection with malware, please check out this article:
Moving a Website that’s had a malware infection
It may be well worth your while investing in a service like Sucuri premium, Malcare, or a professional WordPress malware clean up service.
9. MySQL is Corrupt
Database corruption can occur when the server has ran out of disk space or if a plugin has caused serious problems. Both of these scenarios are rare, but depending on what’s occurred, the only avenue available to you may restoring a snapshot at your server provider.
9.1 InnoDB Corruption
InnoDB corruption may be something that you can recover from. Here you will see MySQL constantly restarting over and over for seemingly no reason, and the Error Establishing a Database Connection message will be intermittent.
To my knowledge, we’ve only ever seen one case of this particular issue, and it seems that a forced conversion from utf8 to utf8mb4 character type was the cause (and this of course done by a plugin).
Checking the MySQL Log
Here’s what you may see in the MySQL log inside the Server Customizer > Logs tab:
2022-10-12 23:44:29 0 [Note] InnoDB: Buffer pool(s) load completed at 221012 23:44:29
2022-10-12 23:44:41 0x7f88d43ab700 InnoDB: Assertion failure in file /home/buildbot/buildbot/build/mariadb-10.5.4/storage/innobase/data/data0type.cc line 67
InnoDB: Failing assertion: !(prefix_len % mbmaxlen)
InnoDB: We intentionally generate a memory trap.
InnoDB: Submit a detailed bug report to https://jira.mariadb.org/
InnoDB: If you get repeated assertion failures or crashes, even
InnoDB: immediately after the mysqld startup, there may be
InnoDB: corruption in the InnoDB tablespace. Please refer to
InnoDB: https://mariadb.com/kb/en/library/innodb-recovery-modes/
InnoDB: about forcing recovery.
221012 23:44:41 [ERROR] mysqld got signal 6 ;
This could be because you hit a bug. It is also possible that this binary
or one of the libraries it was linked against is corrupt, improperly built,
or misconfigured. This error can also be caused by malfunctioning hardware.
...
Trying to get some variables.
Some pointers may be invalid and cause the dump to abort.
Query (0x7f8868010210): ALTER TABLE `wp_pimwick_gift_card` CHANGE `number` `number` TEXT CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_unicode_ci NOT NULL, CHANGE `recipient_email` `recipient_email` TEXT CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_unicode_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL, CHANGE `recipient_name` `recipient_name` VARCHAR(255) CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_unicode_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL, CHANGE `from` `from` VARCHAR(255) CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_unicode_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL, CHANGE `message` `message` TEXT CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_unicode_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL, CHANGE `delivery_date` `delivery_date` VARCHAR(10) CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_unicode_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL
Connection ID (thread ID): 39
Status: NOT_KILLED
InnoDB Recovery
Before you run an InnoDB recovery, you should create a snapshot of the server at the provider level first and then log in as root via SSH to follow the steps below.
Step 1. Stop MySQL
Before you can attempt a recovery, you’ll need to stop MySQL. Stop it with the following command:
systemctl stop mysql
Step 2. Backup all the databases
Next, backup all your databases in their current state using the following command:
cp -a /var/lib/mysql /root/mysql_backup
Step 3. Force Recovery
Edit the config for MySQL using this command:
nano /etc/mysql/mysql.conf.d/mysqld.cnf
Add the following line at the bottom:
innodb_force_recovery = 0
Now save the file with CTRL+O, then exit nano with CTRL+X.
Step 4. Restart MySQL
Now restart MySQL using this command:
systemctl restart mysql
Check if the sites are working normally and that MySQL isn’t restarting every 10/20 seconds (Monit shows the uptime for all services).
If it is still restarting, you have to increase the recovery number from 0 to 1, repeat steps 3 and 4 above with the new value, check the status, and then go up from 1 to 2 or 2 to 3 in case the issue isn’t fixed.
Finishing up: Remove innodb_force_recovery
Once the issue is fixed, edit the config to lower the number back to 0 and restart MySQL.
Finally, edit the file again and remove the line altogether and restart MySQL.
